[an error occurred while processing this directive]
|
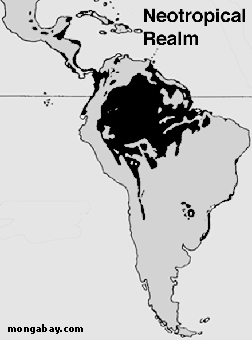
Maps of rainforests in Central and South America
|
|
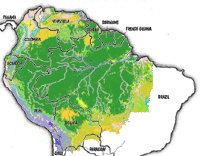
Map of the Amazon basin
|
|
RAINFORESTS IN CENTRAL AND SOUTH AMERICA
The Amazon is the world's largest and most famous rainforest. The Amazon River Basin is roughly the size of the forty-eight contiguous United States (the United States not including Alaska and Hawaii) and includes parts of eight South American countries: Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, and Suriname. The basin is drained by the Amazon River, the world's largest river (and the second longest river after the Nile).
The Amazon is home to more species of plants and animals than any other ecosystem on the planet and perhaps 30% of the world's species are found there. Some of the better known animals found in the Amazon include the jaguar, tapir, and many kinds of monkeys.
The Amazon also supports large populations of tribal people. Today these people, sometimes called Amerindians, have been impacted by the modern world. While they still use on the forest for traditional hunting and gathering, most Amerindians grow crops (like bananas, manioc, and rice), use western goods (like metal pots, pans, and utensils), and make regular trips to towns and cities to bring foods and wares to market.
Outside the Amazon, rainforests are found in coastal Brazil, northern and western South America (from Peru to Venezuela), central America (especially Panama, Costa Rica, Honduras, and Belize), southern Mexico, and on some islands in the Caribbean.
American rainforests are most threatened today with large-scale agriculture (especially soybeans), clearing for cattle pasture, subsistence agriculture by poor farmers, and logging. Every year the Amazon loses an area of forest the size of New Jersey due to these activities
 [an error occurred while processing this directive]
[an error occurred while processing this directive]
|








 [an error occurred while processing this directive]
[an error occurred while processing this directive]